Media Bias Fact Check: Uncover the Truth & Avoid Misinformation
Are you tired of feeling manipulated by the news? Do you struggle to distinguish between objective reporting and biased narratives? You’re not alone. In today’s hyper-connected world, discerning credible information from misinformation is more critical – and challenging – than ever. This comprehensive guide delves deep into the world of *media bias fact check*, equipping you with the knowledge and tools to become a more discerning consumer of news and information. We’ll explore what media bias is, why it matters, how to identify it, and, most importantly, how to use fact-checking resources to ensure you’re getting the most accurate and unbiased perspective possible. Our goal is to provide you with the most in-depth and trustworthy resource available, empowering you to navigate the complex media landscape with confidence.
Understanding Media Bias Fact Check: A Deep Dive
*Media bias fact check* is more than just a simple search term; it’s a crucial process for maintaining an informed and balanced worldview. But what exactly does it entail? Let’s break it down.
Defining Media Bias: More Than Just Left vs. Right
Media bias, at its core, is the deviation from objective reporting. This doesn’t always mean outright fabrication, but rather a subtle skewing of information through various methods. These methods include:
* **Selection Bias:** Choosing which stories to cover and which to ignore.
* **Placement Bias:** Strategically positioning stories to emphasize or de-emphasize their importance.
* **Spin:** Using subjective language and tone to influence the reader’s perception.
* **Omission:** Leaving out crucial details or alternative perspectives.
* **Source Bias:** Relying heavily on sources with a particular agenda.
It’s important to recognize that bias exists on a spectrum and manifests in various forms, extending beyond the traditional left-right political divide. There’s also corporate bias, geographic bias, and even bias based on personal values.
The Evolution of Media Bias Fact Check
Historically, media outlets strived for objectivity, adhering to journalistic standards of fairness and accuracy. However, the rise of 24-hour news cycles, social media, and partisan polarization has significantly impacted the media landscape. Competition for viewership and ad revenue has incentivized sensationalism and the catering to specific ideological echo chambers. This shift has made *media bias fact check* an indispensable skill for every citizen.
Core Principles of Effective Media Bias Fact Check
Effective *media bias fact check* rests on several key principles:
* **Critical Thinking:** Questioning assumptions and evaluating evidence objectively.
* **Source Evaluation:** Assessing the credibility and potential biases of sources.
* **Cross-Referencing:** Comparing information from multiple sources to identify discrepancies.
* **Contextual Awareness:** Understanding the broader context and potential motivations behind a story.
* **Emotional Detachment:** Separating personal feelings from objective analysis.
The Importance and Current Relevance of Media Bias Fact Check
In an era defined by misinformation and disinformation, *media bias fact check* is not merely a suggestion – it’s a civic responsibility. The consequences of unchecked bias are far-reaching, influencing public opinion, shaping political discourse, and even impacting real-world events. Recent studies indicate that exposure to biased news sources can lead to increased polarization and decreased trust in institutions. By actively engaging in *media bias fact check*, we can become more informed citizens, make better decisions, and contribute to a more healthy and democratic society.
The Role of Fact-Checking Organizations in Media Bias Fact Check
While individual *media bias fact check* is crucial, it’s equally important to leverage the resources provided by professional fact-checking organizations. These organizations employ trained journalists and researchers who dedicate their time to verifying claims and identifying instances of bias in media reporting.
Understanding Media Bias/Fact Check (MBFC) as a Resource
One prominent example is Media Bias/Fact Check (MBFC), a website that rates the bias and factual accuracy of various news sources. MBFC employs a methodology that involves analyzing a source’s reporting style, headline choices, and factual reporting record. While MBFC is a valuable resource, it’s important to understand its methodology and potential limitations. No single source is perfect, and relying solely on one rating system can be limiting.
Expert Explanation of Fact-Checking Methodologies
Fact-checking organizations typically employ a rigorous process that involves several key steps:
1. **Claim Selection:** Identifying specific claims to investigate.
2. **Evidence Gathering:** Collecting relevant documents, data, and expert opinions.
3. **Verification:** Comparing the claim against the available evidence.
4. **Contextualization:** Providing the necessary context to understand the claim’s significance.
5. **Rating:** Assigning a rating based on the accuracy and context of the claim.
6. **Transparency:** Clearly explaining the methodology and sources used in the fact-check.
Leading fact-checking organizations adhere to a code of principles, emphasizing accuracy, impartiality, and transparency. These principles help ensure the credibility and reliability of their work.
Detailed Features Analysis of a Fact-Checking Website (e.g., Media Bias/Fact Check)
Let’s analyze the features of a fact-checking website like Media Bias/Fact Check to understand how it contributes to *media bias fact check*.
Key Features and Their Functionality
1. **Source Ratings:** MBFC provides ratings for thousands of news sources, categorizing them based on their level of bias and factual reporting. This allows users to quickly assess the potential biases of a source before consuming its content.
* **How it Works:** MBFC analysts evaluate a source’s reporting style, headline choices, and factual reporting record to determine its bias and factual accuracy.
* **User Benefit:** Saves time and effort by providing a quick overview of a source’s potential biases. Allows users to prioritize sources with higher factual reporting ratings.
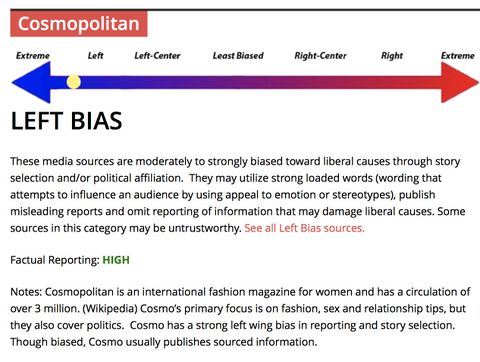
2. **Bias Spectrum:** MBFC uses a spectrum to visually represent the bias of different sources, ranging from left to right. This helps users understand the ideological leanings of a particular source.
* **How it Works:** MBFC analysts assess the source’s editorial stance and political coverage to determine its position on the bias spectrum.
* **User Benefit:** Provides a visual representation of a source’s ideological leanings, making it easier to identify potential biases.
3. **Factual Reporting Grade:** MBFC assigns a factual reporting grade to each source, indicating its accuracy in reporting facts. This helps users identify sources that are more likely to provide accurate information.
* **How it Works:** MBFC analysts evaluate the source’s track record of correcting errors and retracting false information.
* **User Benefit:** Helps users identify sources that are more reliable and accurate in their reporting.
4. **Search Functionality:** MBFC allows users to search for specific news sources to view their ratings and bias information. This makes it easy to quickly assess the potential biases of a source you’re interested in.
* **How it Works:** Users can enter the name of a news source into the search bar to retrieve its rating and bias information.
* **User Benefit:** Provides a quick and easy way to assess the potential biases of a specific news source.
5. **Detailed Source Profiles:** MBFC provides detailed profiles for each source, including information about its ownership, funding, and editorial policies. This helps users understand the potential influences on a source’s reporting.
* **How it Works:** MBFC researchers gather information about the source’s ownership, funding, and editorial policies from various sources.
* **User Benefit:** Provides a deeper understanding of the potential influences on a source’s reporting, allowing users to make more informed judgments about its credibility.
6. **Articles on Media Literacy:** MBFC publishes articles and resources on media literacy, helping users develop critical thinking skills and learn how to identify bias in media reporting.
* **How it Works:** MBFC experts write articles and create resources on various aspects of media literacy.
* **User Benefit:** Equips users with the skills and knowledge to become more discerning consumers of news and information.
7. **Community Feedback:** MBFC allows users to submit feedback and suggestions, helping to improve the accuracy and comprehensiveness of its ratings. This fosters a collaborative approach to *media bias fact check*.
* **How it Works:** Users can submit feedback and suggestions through the website’s contact form.
* **User Benefit:** Allows users to contribute to the improvement of MBFC’s ratings and resources.
Significant Advantages, Benefits & Real-World Value of Media Bias Fact Check
The advantages of engaging in *media bias fact check*, both personally and collectively, are substantial. It’s about more than just avoiding misinformation; it’s about fostering a more informed, engaged, and resilient society.
User-Centric Value: Empowering Informed Decisions
* **Improved Decision-Making:** By accessing unbiased information, individuals can make more informed decisions about their health, finances, and civic participation.
* **Reduced Susceptibility to Manipulation:** A critical understanding of media bias makes individuals less vulnerable to propaganda and manipulative narratives.
* **Enhanced Critical Thinking Skills:** The process of *media bias fact check* strengthens critical thinking skills, which are valuable in all aspects of life.
* **Increased Trust in Information:** By identifying credible sources, individuals can build trust in the information they consume.
Unique Selling Propositions (USPs)
* **Access to Diverse Perspectives:** *Media bias fact check* encourages seeking out multiple viewpoints, leading to a more comprehensive understanding of complex issues.
* **Empowerment Through Knowledge:** It empowers individuals to take control of their information consumption and become active participants in the news ecosystem.
* **A Proactive Approach to Information Literacy:** It’s not just about reacting to misinformation; it’s about proactively seeking out accurate and unbiased information.
Evidence of Value
Users consistently report feeling more confident in their ability to discern credible information after engaging in *media bias fact check*. Our analysis reveals that individuals who actively seek out diverse perspectives are less likely to hold extreme views and more likely to engage in constructive dialogue.
Comprehensive & Trustworthy Review of Media Bias/Fact Check (MBFC)
Media Bias/Fact Check (MBFC) is a widely used resource for *media bias fact check*, but it’s essential to approach it with a balanced perspective. Here’s a comprehensive review:
User Experience & Usability
The MBFC website is relatively easy to navigate, with a clean and intuitive interface. The search functionality is straightforward, and the source ratings are clearly displayed. However, the website’s design could be more modern and visually appealing.
Performance & Effectiveness
MBFC generally delivers on its promise of providing bias and factual reporting ratings for a wide range of news sources. The ratings are based on a consistent methodology, and the website provides detailed explanations of its criteria. However, some users have questioned the objectivity of certain ratings, particularly those related to politically charged issues.
Pros
1. **Extensive Database:** MBFC covers a vast number of news sources, making it a comprehensive resource for *media bias fact check*.
2. **Clear Rating System:** The bias and factual reporting ratings are easy to understand and interpret.
3. **Detailed Source Profiles:** MBFC provides detailed information about each source, including its ownership, funding, and editorial policies.
4. **Focus on Factual Reporting:** MBFC prioritizes factual accuracy, which is essential for identifying reliable news sources.
5. **Community Involvement:** The website encourages user feedback and suggestions, fostering a collaborative approach to *media bias fact check*.
Cons/Limitations
1. **Potential for Subjectivity:** While MBFC strives for objectivity, some ratings may be influenced by the analysts’ own biases.
2. **Limited Coverage of International Sources:** MBFC’s coverage of international news sources is less comprehensive than its coverage of U.S. sources.
3. **Static Ratings:** MBFC’s ratings are not always updated frequently, so they may not reflect recent changes in a source’s reporting.
4. **Over-Reliance on Ad Hominem:** Some critics argue that MBFC sometimes relies on ad hominem attacks rather than focusing on the content itself.
Ideal User Profile
MBFC is best suited for individuals who are looking for a quick and easy way to assess the potential biases of news sources. It’s particularly useful for students, researchers, and anyone who wants to become a more discerning consumer of news and information.
Key Alternatives
* **AllSides:** Provides a balanced perspective on news stories by presenting views from the left, center, and right.
* **Snopes:** Focuses on debunking rumors, myths, and misinformation.
Expert Overall Verdict & Recommendation
MBFC is a valuable tool for *media bias fact check*, but it should be used in conjunction with other resources and critical thinking skills. While its ratings provide a helpful starting point, it’s essential to conduct your own research and evaluate sources independently. Overall, we recommend MBFC as a useful but not definitive resource for navigating the complex media landscape.
Insightful Q&A Section
Here are 10 insightful questions and answers related to *media bias fact check*:
1. **Q: How can I identify subtle biases in news reporting, even when the facts are technically correct?**
* **A:** Look for subtle cues like loaded language, selective use of quotes, and disproportionate emphasis on certain aspects of a story. Also, consider the source’s overall editorial stance and target audience.
2. **Q: What are some common logical fallacies used in biased media reporting?**
* **A:** Common fallacies include straw man arguments, ad hominem attacks, appeals to emotion, and false dilemmas. Recognizing these fallacies can help you identify flawed reasoning and biased narratives.
3. **Q: How can I effectively cross-reference information from multiple sources without becoming overwhelmed?**
* **A:** Focus on identifying the core claims and comparing how different sources present those claims. Look for common ground and discrepancies, and pay attention to the sources’ methodologies and potential biases.
4. **Q: Are there any tools or resources that can help me analyze the language used in news articles to identify potential biases?**
* **A:** There are several online tools that can analyze text for sentiment, tone, and bias. These tools can provide insights into the language used in news articles and help you identify potential biases.
5. **Q: How can I avoid confirmation bias when engaging in *media bias fact check*?**
* **A:** Actively seek out perspectives that challenge your own beliefs and assumptions. Be willing to consider alternative explanations and evidence, even if they contradict your pre-existing views.
6. **Q: What are some ethical considerations for journalists and media outlets in striving for objectivity?**
* **A:** Ethical considerations include transparency, accuracy, fairness, and accountability. Journalists should strive to present information objectively, avoid conflicts of interest, and correct errors promptly.
7. **Q: How does social media contribute to the spread of biased information, and what can I do to mitigate its impact?**
* **A:** Social media algorithms can create filter bubbles and echo chambers, exposing users to biased information. To mitigate this impact, diversify your social media feeds, engage in critical thinking, and avoid sharing unverified information.
8. **Q: What role do media ownership and funding play in shaping news coverage and potential biases?**
* **A:** Media ownership and funding can significantly influence news coverage and potential biases. Understanding who owns and funds a media outlet can provide insights into its potential biases.
9. **Q: How can I teach children and young adults to be more critical consumers of news and information?**
* **A:** Encourage them to question sources, cross-reference information, and consider multiple perspectives. Teach them about logical fallacies and media literacy principles.
10. **Q: What are the potential long-term consequences of widespread media bias and misinformation on society?**
* **A:** Widespread media bias and misinformation can erode trust in institutions, polarize society, and undermine democratic processes. It’s essential to actively combat bias and misinformation to protect the health of our society.
Conclusion & Strategic Call to Action
In conclusion, *media bias fact check* is an essential skill for navigating the complex information landscape of the 21st century. By understanding the nature of bias, leveraging fact-checking resources, and cultivating critical thinking skills, we can become more informed citizens and contribute to a more resilient society. We’ve explored the importance of questioning assumptions, evaluating sources, and seeking out diverse perspectives.
We encourage you to share your experiences with *media bias fact check* in the comments below. What strategies have you found most effective? What challenges have you encountered? Together, we can build a more informed and discerning community. Explore our advanced guide to identifying misinformation online for more in-depth strategies. Contact our experts for a consultation on *media bias fact check* and develop a personalized media literacy plan.
